Before we get in to all of the details and specifics, the quick answer is YES!!!
Many homeowners don’t know what or where a heat exchanger is until something goes wrong with theirs. When your furnace is in good working order, it’s easy to forget that the heat exchanger is the largest component of the furnace. Like all man-made devices, time and use take their toll on heat exchangers, and can result in a cracked heat exchanger or holes forming. When this happens, the result can be a furnace that produces incomplete fuel combustion and unacceptable levels of carbon monoxide (CO), a potentially unsafe condition.

A cracked heat exchanger found by one of our professional TMS technicians.
How Does a Heat Exchanger Work?
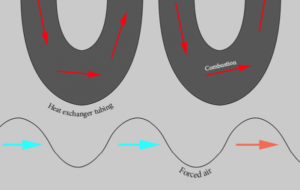
Heat exchangers, metal shells and tubes, work by transferring heat from one place to another. When a furnace burns natural gas or propane fuel, its exhaust/combustion by-products (also known as flue gas) enter and travel through the heat exchanger. The hot flue gas heats the metal as the gas makes its way to the exhaust outlet of the furnace. As this is happening, the hot metal heats the air circulating over the exterior of the heat exchanger.
Health Risks
Because the heat exchanger contains the flue gas inside of itself, it is important there are no holes, cracks or other deterioration. This type of deterioration that permits leakage and mixing of flue gas with the air being heated can result in incomplete combustion and the formation of carbon monoxide and other harmful by-products. Although your furnace may not immediately leak carbon monoxide into the living space, high CO levels make it unsafe to operate.
Once the first crack appears, you have a problem. While the furnace can still function at reduced efficiency, the combustion gases and by-products are no longer completely contained. Natural gas exposure alone, in small amounts, can cause headaches, nausea, or breathing issues. The most common by-products that can leak from a furnace are:
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) – Colorless and odorless, initial symptoms include headaches, weakness and vomiting. And longer exposure can be fatal.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) – A harsh and saccharine gas, short term exposure can cause coughing, bronchitis, and inflammation of the lungs’ lining.
- Particulate Matter (PM) – Particles that can cause a variety of ailments depending on the size, from asthma to irregular heartbeat.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) – A heavy and colorless gas, CO2 causes vertigo and seizures at high concentrations.
Detect Heat Exchanger Problems
Unless your furnace is malfunctioning or your carbon monoxide detector is going off, it’s nearly impossible to know if your heat exchanger has developed problems without direct inspection or testing for CO. This is why regular maintenance is very important. An inspection and a combustion analysis/CO test is the best way to determine whether the furnace is operating safely.
Understanding the potential risks of a damaged heat exchanger is the first step towards a safe heating season. The second step is a solid maintenance schedule with a full fall checkup that will ensure your gas-supplied HVAC units are crack-free.
CALL US to schedule your maintenance and thorough inspection with one of our professional TMS technicians to ensure that your heating system is running SAFELY and is ready to keep you and your home comfortable when you turn it on for the season.
Sources: https://www.standardheating.com/2018/03/19/ask-expert-heat-exchanger/ & https://www.ressacclimatecontrol.com/a-cracked-heat-exchanger-what-it-means-and-what-to-do/